You’ve agreed on a $10,000 crypto deal with someone you met online. The terms are set, you’re both excited — but now comes the awkward question that kills countless crypto transactions:
Who sends first?
Read more: What is Crypto Escrow? The Complete Guide for 2026If you’re the buyer, you worry about sending money and never receiving what you paid for. If you’re the seller, you worry about delivering your work or goods and never getting paid. It’s a classic standoff that has plagued peer-to-peer transactions since the dawn of online commerce.
Traditional solutions don’t work well in crypto. PayPal has chargebacks that favor buyers unfairly. Bank wires are irreversible and favor sellers. And trusting a stranger? That’s just gambling with extra steps.
This is exactly why crypto escrow exists.
In this complete guide, you’ll learn what crypto escrow is, how it works on a technical level, the different types available, and how to choose the right service for your needs. Whether you’re a freelancer getting paid in USDC, an OTC trader swapping large amounts, or simply curious about Web3 payment protection — this guide has you covered.
Table of Contents
- What is Escrow? (Traditional vs Crypto)
- How Crypto Escrow Works: Step by Step
- Types of Crypto Escrow
- Why Use Crypto Escrow?
- Common Use Cases
- Risks and Considerations
- How to Choose a Crypto Escrow Service
- FAQ
What is Escrow? (Traditional vs Crypto)
Before diving into the crypto-specific details, let’s understand what escrow means in general.
Escrow is a financial arrangement where a neutral third party holds funds until both buyer and seller fulfill their obligations.
Think of it as a trust bridge. Neither party has to go first because the money sits safely in the middle, released only when everyone’s happy.
How Traditional Escrow Works
In the traditional world, escrow typically involves:
- A licensed escrow company that holds funds in a regulated account
- Legal agreements that specify exactly when funds are released
- Human verification of document delivery, inspections, or milestones
- Fees ranging from 1-3% with minimum charges often starting at $300-500
You’ve probably encountered escrow when buying a house. The title company holds your down payment until the deed transfers. It works, but it’s slow, expensive, and designed for large, infrequent transactions.

How Crypto Escrow Works
Crypto escrow replaces the trusted company with something even better: code that neither party controls.
Instead of a bank or title company, funds are locked in a smart contract — a self-executing program on the blockchain that releases funds automatically when conditions are met.
Here’s the key difference:
| Aspect | Traditional Escrow | Crypto Escrow |
|---|---|---|
| Trust model | Trust the company | Trust the code |
| Custody | Company holds funds | Smart contract holds funds |
| Availability | Business hours only | 24/7/365 |
| Transparency | Opaque internal processes | Fully auditable on-chain |
| Fees | 1-3% with high minimums | Often 1% with low/capped fees |
| Speed | Days to weeks | Minutes to hours |
| Jurisdiction | Limited by borders | Global, permissionless |
With crypto escrow, there’s no human middleman who can freeze your funds, lose your paperwork, or disappear with your money. The rules are written in code, visible to everyone, and executed exactly as programmed.
How Crypto Escrow Works: Step by Step
Let’s walk through a typical crypto escrow transaction from start to finish.
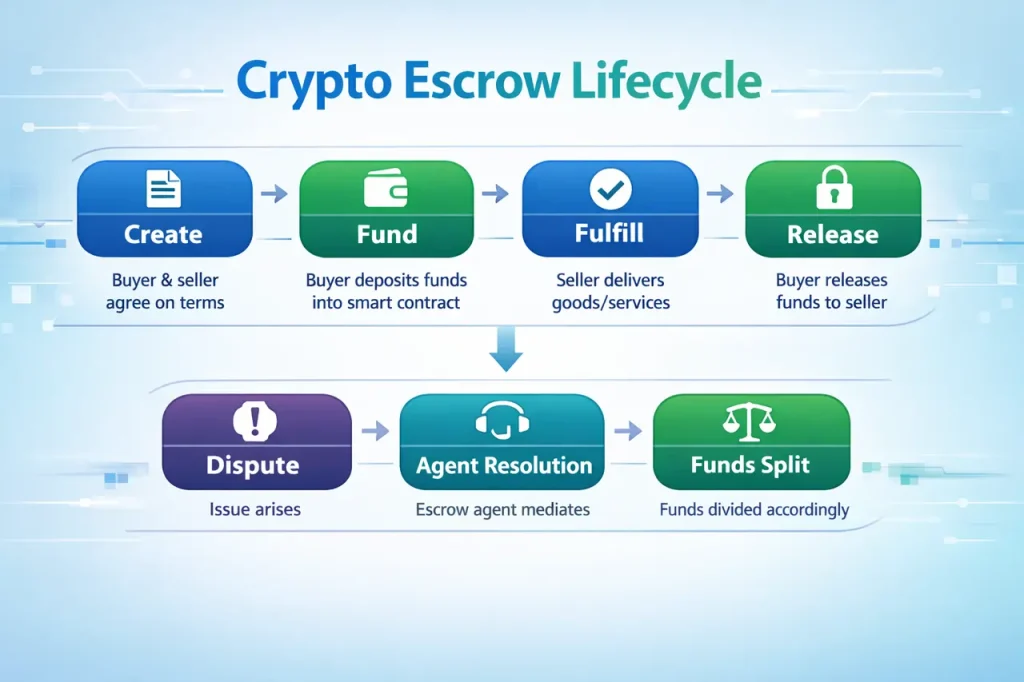
Step 1: Agreement
Before any funds move, buyer and seller agree on the terms off-chain. This typically includes:
- What’s being delivered (product, service, digital goods)
- Price and payment token (USDC, USDT, ETH, etc.)
- Timeline for delivery and review
- Success criteria — how do both parties know the job is done?
- What happens if things go wrong — dispute process, refund conditions
Good escrow platforms let you generate a formal agreement document that both parties sign. This document’s hash (a cryptographic fingerprint) is stored on-chain, creating an immutable record of what was agreed.
Step 2: Funding the Escrow
With terms agreed, the buyer creates the escrow by:
- Connecting their Web3 wallet
- Entering the transaction details (amount, seller’s wallet address, agent if applicable)
- Approving the token spending
- Depositing funds + paying the protocol fee
Once the transaction confirms, the funds are locked in the smart contract. The buyer can no longer spend them, but the seller can’t access them either. They sit in cryptographic limbo, controlled only by the escrow’s predefined rules.
💡 Pro tip: The escrow address is often deterministic — meaning it can be calculated before the escrow even exists. This allows the agreement PDF to include the exact contract address for verification.
Step 3: Seller Accepts
The seller reviews the escrow terms and must explicitly accept to activate it. This prevents situations where someone creates an escrow with incorrect terms and expects the seller to just go along with it.
If the seller declines (or doesn’t respond within the acceptance window), the buyer gets their funds back automatically.
Step 4: Fulfillment
With the escrow active, the seller delivers the goods or completes the service. Once done, they mark the escrow as “Fulfilled” in the platform.
This signals to the buyer: “Hey, I’ve done my part. Your turn to review.”
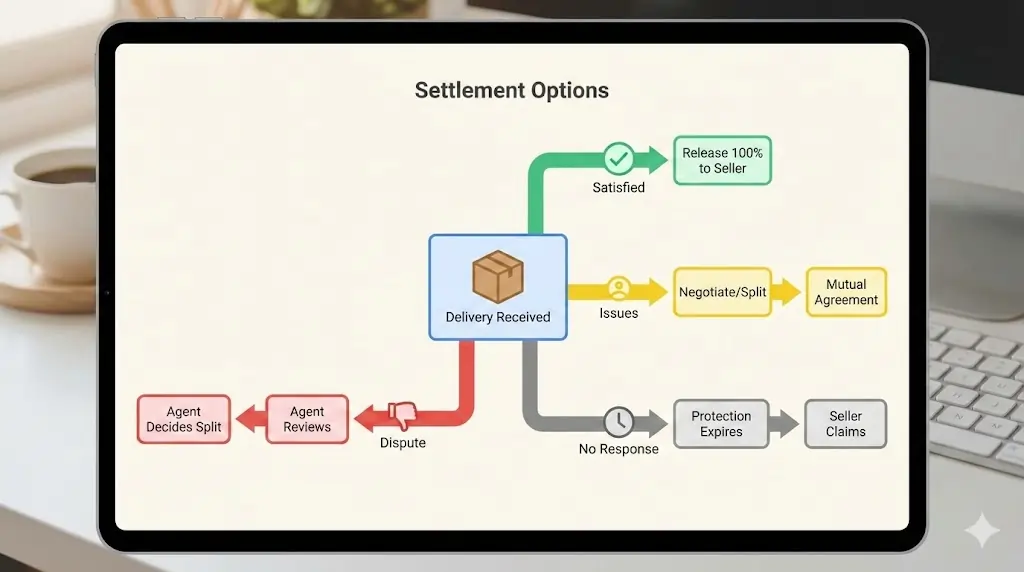
Step 5: Release or Dispute
The buyer now has a protection period to review the delivery. During this time, they can:
- ✅ Release — If satisfied, release 100% of funds to the seller instantly
- 🔄 Request changes — Work with the seller to make adjustments
- ❌ Open a dispute — If there’s a significant problem
If the buyer does nothing and the protection period expires? The seller can claim the funds. This prevents buyers from ghosting after receiving their delivery.
Types of Crypto Escrow
Not all crypto escrow is created equal. There are several models, each with different trust assumptions and tradeoffs.
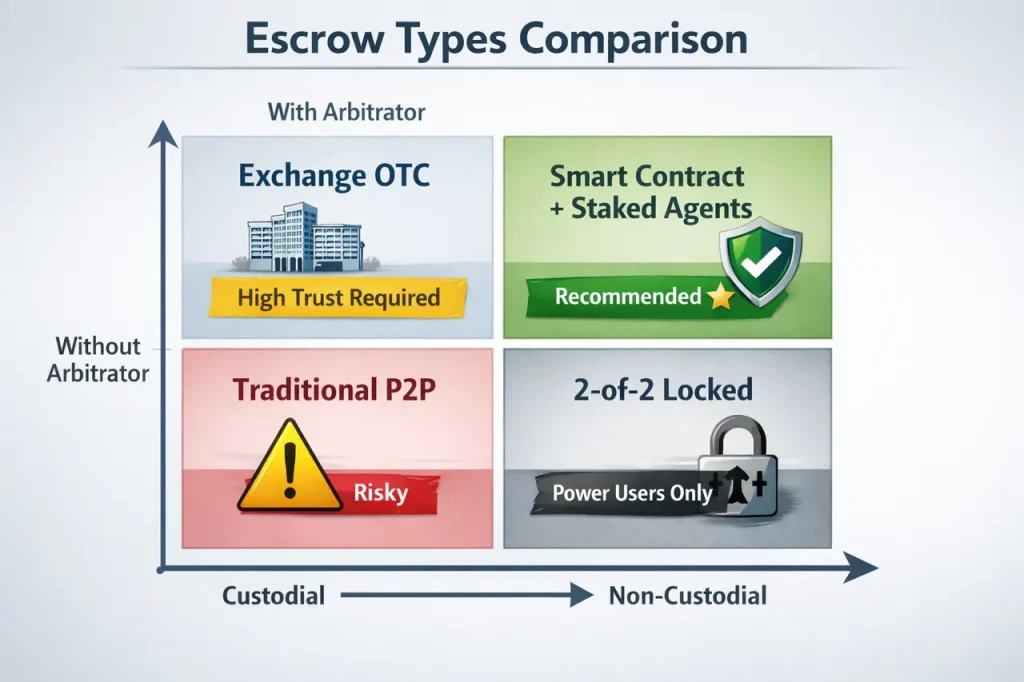
Custodial Escrow (Centralized)
How it works: A company (like an exchange) holds the crypto in their own wallets. They manually review disputes and release funds based on their judgment.
Pros:
- Familiar user experience
- Human customer support
- Can integrate fiat payments
Cons:
- You must trust the company not to steal, freeze, or lose funds
- Single point of failure (hack = everyone loses)
- Often requires KYC/identity verification
- Higher fees (covering operational costs)
Examples: Exchange OTC desks, traditional escrow companies accepting crypto
Non-Custodial Escrow (Decentralized)
How it works: Smart contracts hold funds with no single party having unilateral control. The code enforces release conditions automatically.
Pros:
- True self-custody until release conditions met
- No single point of failure
- Transparent, auditable rules
- Lower fees possible
- No KYC (wallet-based identity)
Cons:
- Requires Web3 knowledge
- Smart contract bugs are possible (though audits minimize this)
- No “forgot password” recovery
Example: Zenland uses non-custodial smart contracts where funds sit in audited code that neither Zenland nor any third party can access.
2-of-2 Multisig (Locked Escrow)
How it works: Both buyer and seller must agree to release funds. No third party exists — it’s pure game theory.
Pros:
- Maximum trustlessness (no arbiter at all)
- Maximum privacy
- Lowest fees (no agent)
Cons:
- Funds can be locked forever if parties disagree
- No dispute resolution mechanism
- Requires high trust or established relationship
The game theory: This works because of “mutually assured destruction.” If the seller cheats, the buyer refuses to release and the money burns (locked forever). If the buyer cheats, the seller refuses to refund. Cheating has zero expected value, incentivizing honest behavior.
Best for: OTC trades between established partners, high-trust relationships, philosophical preference for zero third parties.
2-of-3 Multisig with Arbitrator
How it works: Three keys exist — buyer, seller, and arbitrator. Any two can release funds. In normal operation, buyer and seller settle directly. If they disagree, the arbitrator sides with one party.
Pros:
- Dispute resolution exists
- Arbitrator can’t steal funds (needs one other key)
- Flexible resolution
Cons:
- Must trust the arbitrator to be fair and available
- Arbitrator could collude with one party
- Often manual, off-chain process
Example: Bitrated (for Bitcoin)
Smart Contract Escrow with Staked Agents
How it works: Similar to 2-of-3 multisig, but agents stake their own funds as collateral. If they misbehave, they can be penalized (slashed) by the protocol’s governance.
Pros:
- Agents have skin in the game
- Stake limits how much value they can arbitrate (MAV)
- DAO oversight provides accountability
- On-chain transparency
Cons:
- Slightly more complex
- Agent fees apply in disputes
This is the model Zenland uses. Agents stake funds that determine their Maximum Arbitratable Value (MAV) — they can only handle disputes for escrows within their stake limits. This prevents an agent from making one massive corrupt decision and disappearing.
Why Use Crypto Escrow?
Still wondering if you need escrow? Here are the key benefits:
1. Protection Against Scams
The crypto space is rife with scammers. Escrow neutralizes most scam tactics because:
- Sellers can’t take money without delivering
- Buyers can’t take delivery without paying
- Fake “payment sent” screenshots are worthless
2. No Chargebacks (Seller Protection)
Unlike credit cards or PayPal, crypto payments are irreversible. But this cuts both ways — buyers have no recourse if scammed. Escrow protects buyers while maintaining the no-chargeback property sellers love.
3. Global, 24/7 Availability
Traditional escrow operates on business hours and struggles with cross-border transactions. Crypto escrow works:
- At 3 AM on Christmas
- Between parties in different countries
- Without caring about bank holidays
4. Lower Fees for Large Transactions
Traditional escrow fees are percentage-based with no cap. Crypto escrow often has maximum fee limits. On Zenland, for example, the fee is 1% with a $50 maximum cap. That means a $100,000 transaction costs the same $50 as a $5,000 transaction — massive savings for high-value deals.
5. Transparency
Every action in a smart contract escrow is recorded on-chain. Both parties can verify:
- Funds were deposited
- When actions were taken
- Exactly what was paid out
No “the check is in the mail” uncertainty.
Common Use Cases
Crypto escrow shines in situations where trust is low and stakes are high.
Freelance & Service Payments
The scenario: You hire a developer from Discord to build a smart contract. You’ve never met them. They’ve never worked with you.
Without escrow: Someone has to go first. Freelancers routinely get ghosted after delivering. Clients routinely get rugged after paying upfront. “50% now, 50% on delivery” still leaves exposure.
With escrow: Client funds the full amount. Developer works knowing payment is secured. Client releases on satisfactory completion. Everyone sleeps better.
OTC (Over-the-Counter) Trades
The scenario: You want to buy $50,000 of ETH off-exchange to avoid slippage. You found a seller in a Telegram group.
Without escrow: This is peak “who sends first” territory. Large amounts, anonymous parties, irreversible transactions. Recipe for disaster.
With escrow: Both parties deposit. Simultaneous swap when conditions are met. Even if you’re trading with “TrustMeBro420,” the code ensures fairness.
NFT Sales (Off-Marketplace)
The scenario: You’re selling a rare NFT directly to a collector for 15 ETH. You don’t want marketplace fees.
Without escrow: Send NFT first and hope they pay? Or ask for payment first and hope they trust you? Neither is great.
With escrow: Buyer locks payment, seller transfers NFT, buyer confirms receipt, payment releases. Clean and safe.
Domain Name Sales
The scenario: You’re selling a premium crypto domain (zenland.eth) for $10,000.
Without escrow: Same trust problem. Plus domain transfer can be complex.
With escrow: Payment locked until domain transfer is verified (potentially with oracle integration or manual verification).
Real Estate (Tokenized)
The scenario: You’re buying a tokenized share in real estate using USDC.
With escrow: Handles the complexity of multiple parties, legal requirements, and large sums while maintaining blockchain rails.
Risks and Considerations
Crypto escrow isn’t magic. Here are the risks to understand:
Smart Contract Bugs
Code can have bugs. A flaw in the escrow contract could potentially:
- Lock funds permanently
- Allow unauthorized withdrawals
- Create unexpected behaviors
Mitigation: Use platforms with audited contracts from reputable security firms. Check that contracts are verified on block explorers. Prefer battle-tested protocols over new ones.
Platform Risk (For Custodial)
If you’re using custodial escrow, you’re trusting a company. They could:
- Get hacked
- Freeze your funds due to regulatory pressure
- Simply disappear (rug pull)
Mitigation: Use non-custodial escrow where smart contracts hold funds. No company access = no company risk.
Dispute Resolution Quality
If a dispute arises, the resolution is only as good as the arbiter:
- Inexperienced arbiters may make poor decisions
- Biased arbiters could favor one party
- Slow response times drag out resolution
Mitigation: Choose platforms with staked agents (skin in the game), clear reputation metrics, and DAO oversight for accountability.
Gas Fees (On Ethereum)
Creating and settling escrows requires gas. On Ethereum mainnet, this might be $5-50 depending on network congestion.
Mitigation: For small transactions, consider whether gas costs make escrow worthwhile. Some platforms optimize gas through factory patterns and minimal proxies. Layer 2 solutions can also reduce costs significantly.
User Error
Smart contracts do exactly what you tell them. If you:
- Send to the wrong address
- Enter wrong amounts
- Accept bad terms without reading
…there’s no “undo” button.
Mitigation: Always double-check addresses, amounts, and terms before confirming transactions.
How to Choose a Crypto Escrow Service
Not all escrow services are equal. Here’s a checklist for evaluation:

Security Audit Status
- Has the smart contract been audited by a reputable firm?
- Are audit reports publicly available?
- Have any critical issues been found and fixed?
Fee Transparency
- What’s the percentage fee?
- Are there minimum or maximum caps?
- Who pays — buyer, seller, or split?
- Are there hidden fees for disputes?
Dispute Resolution Mechanism
- Who resolves disputes?
- What’s their incentive to be fair?
- How long does resolution typically take?
- Is there accountability for bad decisions?
Supported Tokens and Chains
- Does it support the tokens you use? (USDC, USDT, ETH, etc.)
- What blockchain(s) does it run on?
- Are there Layer 2 options for lower fees?
Contract Verification
- Can you view verified source code on Etherscan?
- Is the project open source?
- Can you independently verify the rules?
User Experience
- Is the interface intuitive?
- Is there documentation/support?
- What’s the track record and community reputation?
Zenland: Non-Custodial Escrow Done Right
If you’re looking for a crypto escrow service that checks all the boxes, Zenland offers:
- 100% non-custodial — funds in audited smart contracts, not company wallets
- 1% fee, $50 max cap — high-value transactions don’t get punished
- Staked agents — arbitrators have skin in the game with MAV limits
- DAO governed — community oversight, not corporate decisions
- Stablecoin focus — USDC and USDT for price stability
Whether you’re a freelancer securing your next payment or conducting a large OTC trade, Zenland provides the security of code with the flexibility of professional dispute resolution when needed.
💡 Ready to try trustless escrow? Create your first escrow on Zenland →
Frequently Asked Questions
Is crypto escrow safe?
Crypto escrow is as safe as the specific platform and smart contract you use. Non-custodial escrow with audited contracts from reputable platforms is generally very safe. The main risks are smart contract bugs (mitigated by audits) and user error (mitigated by careful verification).
Custodial escrow adds platform risk — you’re trusting a company. Non-custodial escrow eliminates this by having code hold funds.
What happens if there’s a dispute?
In standard escrow with an agent:
- The buyer opens a formal dispute
- Either party invites the pre-selected agent
- Both parties submit evidence
- The agent reviews and decides the fund split
- Funds are distributed automatically
In locked escrow (no agent): Parties must negotiate directly. If they can’t agree, funds remain locked. This is why locked escrow is only recommended for high-trust situations.
How much does crypto escrow cost?
Costs vary by platform:
- Custodial platforms: Often 1-5% with no cap
- Non-custodial platforms: Usually 1% or less
- Zenland: 1% with a $50 maximum cap (and $0.50 minimum)
Plus gas fees for blockchain transactions (typically $5-50 on Ethereum, less on Layer 2).
Can I use Bitcoin for escrow?
Yes, but Bitcoin lacks native smart contracts. Bitcoin escrow typically uses:
- Multisig wallets (2-of-3 with an arbitrator)
- Custodial services
- Time-locked transactions
Ethereum and EVM chains offer more flexible smart contract escrow. For the best experience, stablecoins like USDC or USDT on Ethereum are recommended — you get smart contract flexibility without price volatility.
What tokens does Zenland support?
Currently, Zenland supports USDC and USDT on Ethereum. Additional tokens may be added through DAO governance.
Stablecoins are prioritized because they eliminate price volatility during the escrow period. You don’t want a 20% price swing affecting your deal while waiting for delivery.
What if the buyer disappears after delivery?
In standard escrow: After the seller marks fulfillment, a protection period starts. If the buyer doesn’t release or dispute within this period, the seller can claim the funds automatically.
In locked escrow: The seller would be stuck. This is why locked escrow requires high trust.
Can I cancel an escrow after funding?
It depends on the escrow state:
- Before seller accepts: Buyer can typically cancel and get refunded
- After active: Buyer cannot unilaterally withdraw. The seller must agree to refund, or the dispute process must play out.
This is by design — the seller needs certainty that funds won’t disappear while they’re doing the work.
Is there KYC required?
Most non-custodial escrow platforms, including Zenland, are wallet-based with no KYC requirements. You connect your Web3 wallet and transact pseudonymously.
Custodial platforms often require identity verification due to regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Crypto escrow solves one of the oldest problems in commerce: how do strangers trust each other?
Instead of asking “who sends first?”, escrow lets both parties commit simultaneously. Smart contracts hold funds according to predefined rules. Professional agents provide dispute resolution when needed. And the entire process is transparent, verifiable, and available 24/7 worldwide.
Key takeaways:
- Traditional escrow is slow, expensive, and requires trusting a company
- Crypto escrow uses smart contracts for trustless fund custody
- Non-custodial is safer than custodial (no platform risk)
- Staked agents provide fair dispute resolution with accountability
- Fees are reasonable — often 1% with caps for large transactions
Whether you’re sending $100 for a logo or $100,000 for an OTC trade, crypto escrow gives you the confidence to transact with anyone, anywhere.
Have questions about crypto escrow? Join our community or reach out — we’re happy to help you transact safely.
Last updated: February 2026